ESG: ‘Do as I do, not as I say’
The concept of ESG has been a key driver of fund flows, but most importantly marketing strategies, in recent years. Nearly every fund manager worth their salt has a well-written ESG strategy, outlining its views on the most important issues facing investors, management, and boards. Not to mention the expanding set of “sustainable” and ESG-focused superannuation funds and options, many of which hold questionable underlying investments.
Yet as we know, ESG investing is a matter of individual preference and is incredibly difficult to get right for every single investor or member. It is a world of ‘greys,’ or ‘shades of green,’ if you like.
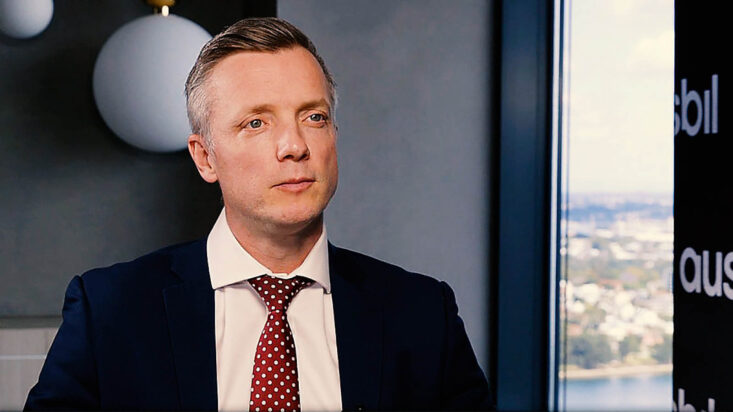
One of the emerging leaders in Australia is Mans Carlsson-Sweeny, who is head of ESG research at Ausbil. He is among the most outspoken investment specialists, and is tasked with the primary role of guiding the group’s ESG assessments and decision-making process. At the recent Morningstar Investment Conference Carlsson-Sweeny offered a clear comparison of views across the industry. The inevitable subject was Rio Tinto Limited.
RIO has remained in the headlines through the destruction of the priceless archaeological asset, showing more than 40,000 years of human presence, that were the caves at Juukan Gorge, despite the company having been told (and knowing) of the significance of the site. The caves were dynamited in order to access $135 million worth of high-grade iron ore. The subsequent departure of senior management (including chief executive officer Jean-Sébastien Jacques) and board members was evidently seen by a number of large investors and super funds as enough self-punishment to warrant the company’s retention within their portfolios. For Carlsson-Sweeny, however, it wasn’t enough, stating that for Ausbil’s Sustainable Equity Fund, RIO “could no longer be held in good conscience.”
He spoke at length about how Rio Tinto had been improving ahead of its indigenous relations disaster, but that its score had been lowered on several occasions, firstly due to “internal governance failures” and secondly, after the Parliamentary inquiry into the disaster highlighted what really occurred. On each occasion the score was reduced, says Carlsson-Sweeny, the holding was reduced such that it was quickly removed from the fund’s top ten holdings and then sold out completely. This despite the team confirming that the “company’s key focuses – aluminium, copper and iron ore – are also all commodities that fare reasonably well in a decarbonised world.”
The decision by Ausbil reflects the complex position in which fund managers and super funds find themselves. Ultimately, they have three options, to sell on principle, to do nothing, or to “actively engage” with management. It seems the majority of the major superannuation funds have chosen the latter option, to engage with management and push for change. Whether they were behind the departure of management is yet to be seen, but “active” engagement is clearly only an option for large and significant investors.
First State Super, now Aware Super, made the interesting choice to remove RIO from its ‘sustainable’ investment options, but not its larger core and balanced funds. AustralianSuper, on the other hand, continues to report an $800 million investment in the company, stating that it has “met with the chair of Rio Tinto and expressed our view that the proposed penalties fall significantly short of appropriate accountability for those responsible,” but apart from that, failing to indicate what response it believes would be sufficient. Subsequently, AustralianSuper has ‘welcomed’ the sacking of the CEO as a sign of the seriousness of the issue.
One of the key challenges facing financial advisers in the era of ESG investing is their role as one of the few remaining client-facing (or member-facing) workers. What COVID-19 has shown is that despite best efforts, fund managers and industry funds simply do not have sufficient resources or skills to liaise directly with the people whose capital they are managing. Financial advisers, on the other hand, are at the coalface, across the desk. When they recommend a product, such as Ausbil, or AustralianSuper, their clients will naturally ask questions about what they hold and why. In a face-to-face context, a twenty-page ESG strategy does little to allay the end-investor’s concerns.